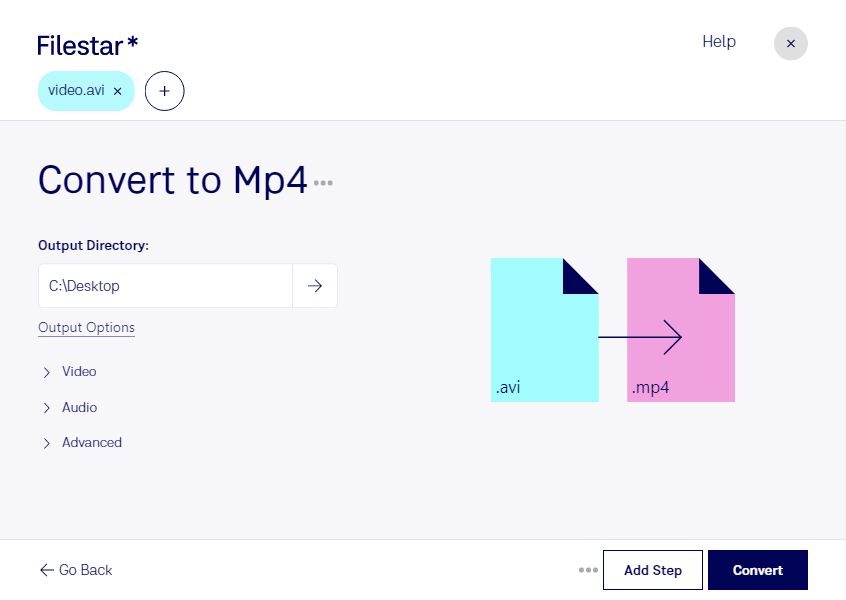
About the Avi file format
- Name
- Audio Video Interleave File
- Extension
- .avi
- Format
- Binary
- Category
- Video
- Developer
- Microsoft
- Description
- An AVI file is a file saved in a multimedia container format created by Microsoft. It stores video and audio data that may be encoded in a variety of codecs such as DivX and XviD. AVI files typically use less compression than similar formats such as .MPEG and .MOV.
- MIME Type
- video/avi
- Sample
- sample.avi
- Wikipedia
- .avi on Wikipedia
The Audio Video Interleave File (AVI) is a container format file format that was introduced by Microsoft in 1992 and uses .avi file extension.
The AVI file comprises of video and audio data files which allow concurrent audio-with-video-playback. Like the counterpart DVD-Video format, AVI file supports the streaming of video and audio though this feature is rarely used.
AVI format falls under the Resource Interchange File Format (RIFF), which has numerous file data divisions as blocks or chunks. The AVI main file is divided into several chunks, with one of them being a single compulsory chunk.
The first chunk has the “hdrl” tag, represents the Metadata and stores information such as width, Frame rate, and height about the video. The second block has the tag “movi2” stores the real audio/visual data of the video. The third optional chunk” idX1” indicates the Offset of the data in the file. Codec software is used to encode and decode the audio/visual data in the second chunk.
Any compression algorithm can be used on the audio/visual data including (Indeo) Intel Real Time, Editable MPEG, and Motion JPEG.
The use of a variety of codecs to encode AVI files is their major downside. One might encounter some problems when opening these files if the specific codec isn’t installed.